2024 Ecommerce SEO Guide
In this guide, we’ll cover the essential elements of ecommerce SEO: keyword research, site structure, and on-page optimization. Boost your store’s visibility rankings with a simple blog post.
Increasing traffic is a major concern for every ecommerce business. But how can you make your online store more attractive to visitors without spending a lot of money on advertising and marketing? The answer is to use ecommerce SEO.
Ecommerce search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of aligning your website with search engine best practices and updating your content to reflect what your customers are searching for.
The benefits that store owners get from SEO include increased traffic, improved brand awareness, and increased sales. However, because search engine algorithms are constantly being updated, it can be difficult to know how to approach search engine optimization.
This guide covers the basics of ecommerce SEO, including how to do keyword research, setting up your site structure, and writing product page content. With this SEO checklist, you’ll be ready to rank and reap the benefits of SEO.
What is eCommerce SEO?
Ecommerce SEO is the process of increasing your online store's visibility on search engine results pages (SERPs).
There are many different tasks involved in ecommerce SEO marketing. It involves creating content that satisfies keyword queries entered into search engines. For example, True Classic , an ecommerce store that sells t-shirts, can improve its website SEO by creating content on “ How to Fold a T-shirt Without Wrinkles .”

Other ecommerce SEO activities include improving page loading speed, writing detailed product descriptions, and securing links from authoritative websites.
Ecommerce websites use SEO as a strategy to generate more traffic and attract visitors who type in queries related to their products and brand.
Why eCommerce Websites Focus on SEO
When you search for something on Google, you are taken to a search engine results page (SERP). There, you will find about 10 results.

These results appear below paid ads (orange) and Google Shopping ads (purple).

Ecommerce SEO is all about ensuring that your product pages appear in the top search results on the first page of Google. Websites that don’t rank in the top 10 are rarely visited, and even those that rank 3 to 5 get far less traffic than the top results.
Additionally, it has been reported that the first result on Google SERP accounts for 27.6% of all clicks. In other words, SEO is very important.

So the key is to rank as high as possible on the first page of search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. This applies not only to product-related searches, but also to searches within your ecommerce niche.
How to Create an Ecommerce SEO Strategy
If you’re new to search engine optimization (SEO) and want to get your store ranked higher on Google, here are six steps you can take to help you set up basic ecommerce SEO on your website.
Ecommerce SEO Steps
- Ecommerce Keyword Research
- eCommerce Site Structure
- Technical SEO
- Ecommerce On-Page SEO
- Blogging
- Link Building
1. Ecommerce Keyword Research
The first step in your ecommerce SEO strategy is to identify the high-value search terms your potential customers are using. To do this, you can conduct ecommerce keyword research, and there are several ways to do it.
Ecommerce keyword research is a little different from traditional keyword research. While most sites only consider informational keywords, ecommerce sites should target both informational and commercial keywords.

People searching for informational keywords are looking for answers, guidance, and explanations. Blogs and content-focused sites value these keywords the most. Ecommerce sites like Shopify also run blogs, but they also target keywords that indicate purchase intent, like “raincoats for dogs.”
Amazon and Google Autocomplete Predictions
When you start typing a search term on Google, the autocomplete feature suggests related searches.

These autocomplete suggestions can be a goldmine of keyword ideas if you already have a few basic keywords in mind (don’t forget to check out related searches at the bottom of the SERP, too).
Amazon Autocomplete Prediction
You can do a similar thing on Amazon. The advantage of Amazon's suggestions is that they are product-centric, unlike Google's, and can include filterable details like price.
 Beware of long-tail keywords. Long-tail keywords describe more specific items, and the longer the keyword, the more specific it is. This means lower competition and often higher conversion rates. Also, Amazon (and other You can see how major ecommerce sites structure their content for visibility in search. Look through their related products menus to get keyword category ideas.
Beware of long-tail keywords. Long-tail keywords describe more specific items, and the longer the keyword, the more specific it is. This means lower competition and often higher conversion rates. Also, Amazon (and other You can see how major ecommerce sites structure their content for visibility in search. Look through their related products menus to get keyword category ideas.
For example, let's say you sell women's fashion items. Look for that category on Amazon. Now you can see the different ways Amazon organizes and sorts its products in that category.

Repeat this process for your other major competitors.
Keyword research tool
For more advanced keyword research, you’ll need a free SEO tool. One of the most popular is Ahrefs .
These tools provide the ability to research and analyze keywords in bulk.
For example, let’s say you’re competing with a quirky t-shirt ecommerce store called BustedTees . Enter that domain into a keyword research tool like Ahrefs and click “Organic keywords” at the top.

Scroll down the page to see all the keywords BustedTees is currently ranking for. You can also check out metrics like search volume and ranking positions. An overview of your competitors’ SERP coverage will help you decide which keywords to compete for.
Choosing the right keywords for your store
Not every ecommerce website can target every keyword. You need to decide which keywords to rank for based on your customers and products. Consider the following factors:
Search Volume
The higher the search volume of a keyword, the more potential traffic it will bring to your site. You can check keyword search volume using free tools like Ahrefs or Google Keyword Planner .
Competition
The lower the competition, the more likely you are to rank for a keyword. SEO tools show keyword difficulty/competition (KD).
Relevancy
How relevant are your product pages or category pages to the search query? This is an important ranking factor that is often overlooked. Focus on keywords that your product can actually satisfy. You can’t fool Google.
Intent
Target keywords that convey the intent to buy or learn about your product. You can usually assess intent by looking at keywords. For example, if you run a store that sells wedding dresses, which search is more relevant: “ball gown wedding dress” or “work dress”?
2. Ecommerce Site Structure
In ecommerce SEO, how your site's pages are organized and structured affects your search engine rankings.
Your site structure also affects your user experience (UX). You want to make it easy for visitors and search engine bots to navigate your store’s content.
Adding or removing products and categories can make your site structure more complex. Before you begin developing your website, make sure you:
- The site structure should be simple and easily scalable as your store grows.
- Every page on your site should be accessible with a few intuitive clicks.
Simplicity is often underestimated. You don’t want your visitors to have to rely on the back button to navigate your site, or to have them wander around in circles trying to find what they’re looking for. You also don’t want to have to restructure and rearrange your site every time you add a new product category.
Most SEO link authority is concentrated on your homepage, as this is the page that other businesses most commonly link to when referring to your website. Therefore, the more clicks a product page gets on your homepage, the less authority it has.
Page Indexing
When implementing SEO on your website, you need to make strategic choices about which web pages to index and rank.
An index is another name for the database that search engines use. So indexing a page means that the page is added to that database. In other words, Google has found the page and added it to search results.

For advice on page indexing, check out these tips from Aleyda Solis, founder of SEO consulting firm Orainti :
Aleyda recommends identifying the types of pages that are worth indexing and optimizing. These pages should serve a real need.
Aleyda says:
“One of the most common problems with ecommerce sites is thin content and content duplication.”
“Thin content is when an ecommerce site doesn’t have a lot of actual text, compared to a blog or software site. Content duplication occurs when the same content appears on multiple product and category pages.”
“Adding blog content to your online store website is a great way to supplement thin content.”
The easiest way to deal with duplicate content is to hide the page from search engines, or noindex it. However, you can also create useful content on that page to make it different, relevant, and competitive.
One way to make a page official is to canonicalize it. Canonicalizing a page is a way to tell Google that the URL you want to show in search results is the “master version.” This is useful in duplicate content situations. Without canonicalization tags, Google can run into the following problems:
- Handling duplicate content can result in missing unique content
- Ranking ability may be diluted
- You may select the wrong master version
Aleyda suggests considering more than just noindex or normalization when you're ready.
“Evaluate whether there are enough search queries about the characteristics of your product to decide whether to index the page,” she says.
“When indexing a page, ask yourself if the page has enough content and if it matches the way users search. You may need to expand and optimize the page to keep it relevant and competitive.”
Aleyda shared a useful chart to visualize the indexing decision process:
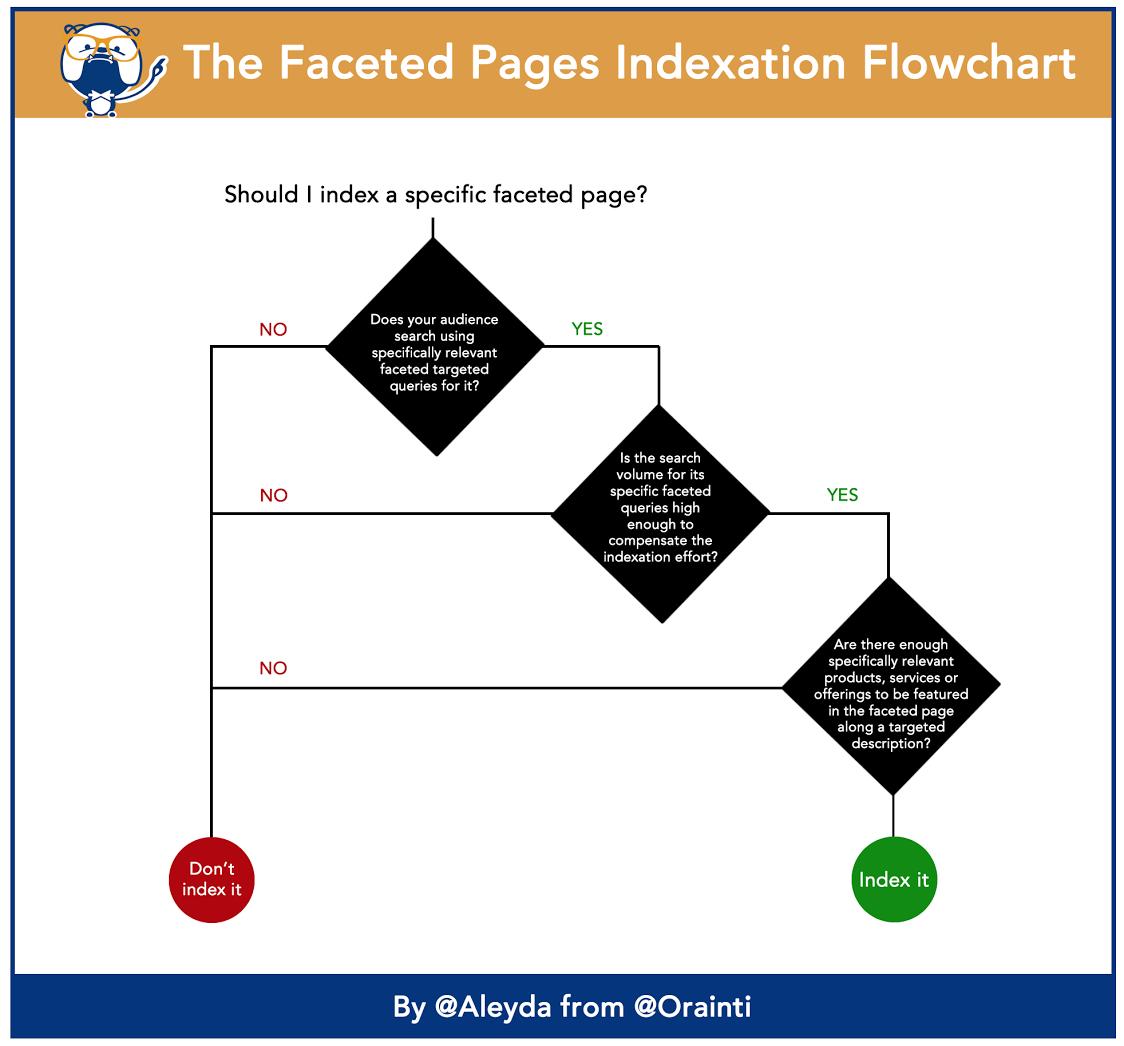
Not every level of your site structure is worth indexing and optimizing, so approach it strategically and refer to the chart above.
Notice how Allbirds uses breadcrumbs to orient the user on their product page. If the user decides not to purchase the Everyday sneakers, they can easily navigate back to 'Men's Shoes' or the homepage to find other products.

Use third-party apps like Category Breadcrumbs to show customers the path they've navigated through your category tree.
3. Technical SEO
Technical SEO is an internal part of search engine optimization that is invisible to shoppers, but ensures that your website is optimized for crawlers, has optimal site speed, and works well on mobile. Technical SEO results in:
- Increase website engagement: Make your site faster and more accessible.
- More organic traffic: Your site is easier to crawl.
Here's how to improve your technical SEO for eCommerce:
- Create a logical internal link structure through menus.
- Submit your sitemap to Google Search Console.
- Optimize your images to load faster.
4. Ecommerce On-Page SEO
Once you’ve completed your keyword research and have your site structure in place, it’s time to optimize the content for the two most valuable page types:
- Product Category Page
- Product Page
Ecommerce Content Basics
If you use Shopify, you probably know that Shopify stores come with a number of SEO features built in. Some of these are provided automatically:
- Contains normalization tags.
- This will generate sitemap.xml and robots.txt files for your website.
- The theme generates a title tag that includes your store name.
- The theme includes social media links and sharing options.
However, other features need to be optimized manually:
- Edit your title tag, meta tags, and meta description to include keywords.
- Edit the alt text of your product images to accurately describe the visual element.
- Include keywords in the file name.
- Consider carefully the URLs for your blog posts, web pages, products, and collections.
When optimizing your title tags and descriptions, your primary goal is to rank on the first page, since you are targeting Google. The secondary goal is to convince searchers to click through to your site.
Including modifiers like “Deals”, “20% Off”, “Free Shipping”, “Wide Selection”, etc. in your meta description can give you a boost and help you target long tail keywords.

eCommerce Product Description
In ecommerce SEO, Google and other search engines use the content of a page to determine which keywords to rank the page for and how high to rank the page for each keyword.
If your product page only has a short description and no other information, Google has little to go on. Copying and pasting descriptions from manufacturers or suppliers is called duplicate content and is not recommended.
Instead, write a unique, comprehensive description that grabs readers’ attention and includes plenty of details about your product. Good on-page content can help improve your product page rankings and reduce overall thin content on your store.
That's why you often see high-ranking search results with product pages that include elements like long descriptions, reviews, etc.

Include relevant keywords and subheadings in every section of each page to help Google understand what your content means.
If you can’t create content for all your products, focus on the ones that are currently ranked lower on the first page. Improving these results can have the biggest impact on conversion rates. The more you do, the more likely you are to see a boost in rankings.
The more content you write, the more accurately Google can rank your page. Customers will also be happy with the added product information. This information may even help them make a purchase.
Using Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) Keywords
LSI keywords are keywords that are closely related to your main keyword. Enter your main keyword into Google Keyword Planner to find related terms and phrases.
You can also find LSI keywords through Amazon searches. Search for your main keyword and check for secondary keywords that appear repeatedly.
For example, let’s say you’re trying to sell blenders. If terms like “14 Speed”, “450W”, and “48oz Glass Jar” appear multiple times, these are likely strong selling points and common elements of search queries.

If you are getting traffic from your primary keywords, try to get to the first page for related secondary keywords as well. It is a good idea to include LSI keywords appropriately in your content.
Create internal links
The longer a visitor explores your site’s content, the greater the chance of a sale. Relevant internal links to other pages on your site help potential customers find information or discover products.
When inserting internal links, you should include your target keyword exactly in the anchor text (the word you are inserting the internal link into). Internal links can help you direct customers to relevant product pages, category pages, and educational content.
Don't overuse internal links. One or two links per few hundred words is fine.
5. Blogging
Blogging is a form of content marketing that uses on-page and technical SEO strategies to increase your website’s search visibility. This helps search engines rank your website as a trustworthy site and rank it for certain keywords. Blogging allows you to leverage SEO to drive a consistent, long-term content strategy.
Every blog post published has the potential to:
- Build a reputation as a trusted source
- Increase the authority of your site
- Increase visibility in organic search
For example, imagine you are starting a business that sells running gear. You want to help your potential customers understand your product, use it more effectively, and solve their running and fitness problems. If you want to be found on search engines like Google, blogging can help.
A well-written blog provides a consistent source of original content for your store. The more people find your content, the more trustworthy you are as a source of information. This will help your rankings. Ecommerce businesses often struggle with blogging because it takes time, effort, and resources. Just posting random blog posts every month won’t bring traffic to your website.
But there are plenty of ecommerce businesses that are doing a good job blogging. For example, retailer Au Lit Fine Linens sells a variety of products for a good night’s sleep, including high-quality bed sheets, pillows, and bath towels. The brand runs a blog called Between the Sheets , which provides helpful articles to readers on how to improve their sleep quality.

The blog is SEO-focused, with the goal of ranking in search engines. Posts often highlight issues readers are having and present Au Lit Fine Linens products as solutions—a nice balance between promotion and information.
When starting a blog for ecommerce SEO, focus on these three elements:
-
Research what keywords you want to rank for. Post content that targets keywords people are likely to search for when they’re solving a problem or making a purchase decision.
-
Optimize your blog posts for SEO. Make sure each blog post is optimized for SEO by targeting specific keywords.
-
Present your product as a solution to a problem. Not every post needs to be about a product, but don’t be afraid to link to a product page when appropriate.
6. Link Building
One of the oldest elements of the Google algorithm is PageRank, a system that attempts to understand the quality of a webpage through the number of links it receives from other websites.
Google uses the number, quality, and relevance of links on a page to determine its credibility. As a result, new websites with few links are rated as less authoritative in the eyes of search engines. This can improve over time, but building quality backlinks can help Google recognize your authority more quickly.
Respected .com, .gov, and .edu sites give the most authority when it comes to providing backlinks. Links from large, well-established websites within your niche are especially valuable.
One link building approach is to focus on partnerships. Determine how you can create content that can provide value to other websites. If you can create something that other people want to use, they will usually cite your content with a link.
Guest Posting
Guest posting can be an effective way to build backlinks by creating content that is relevant to users on other websites. Do some ecommerce keyword research and analyze backlinks with Ahrefs to find sites within your niche that are open to guest posting.
Press reports
Another way to build backlinks to your ecommerce store is through press mentions. Building a press list or hiring a PR firm can be expensive, so here’s a simple way to grow your business that anyone can do.
By signing up for Help A Reporter Out or Help a B2B Writer , you will receive a daily email digest of reporter requests. If the request matches your brand, contact them at the email address provided and pitch them a story. If you do get an interview, don’t forget to ask for a backlink to your website.
Best eCommerce SEO Tools
- Avada SEO & Image Optimizer
- SEOAnt
- Google Analytics
- Ahrefs
Avada SEO & Image Optimizer

Avada SEO is a plugin that helps ecommerce stores outperform their competitors. The plugin offers a variety of technical features to keep your website search-optimized, including image compression, site speed optimization, and schema markup. It also offers 24/7 customer support.
SEOAnt

SEOAnt is a free tool that you can use to run SEO audit reports, fix broken links, and optimize image sizes. It also offers AI features for writing meta and ALT text.
Google Analytics

If you run a website, you probably use Google Analytics. This free SEO tool tracks and reports on your website traffic, giving you the insights you need to better understand your customers, optimize your SEO, and improve your marketing ROI. Shopify store owners can connect Google Analytics to Shopify Analytics and track specific ecommerce data.
Ahrefs

You’ve already seen Ahrefs in action in this post, but it’s worth taking a deeper look at some of its key features. Ecommerce marketing professionals use Ahrefs to create SEO campaigns and rank higher on Google.
Ahrefs is a competitor to other SEO software companies like Moz and Semrush, and is a tool you may come across when researching SEO tools.
You can use Ahrefs to analyze your website’s link profile, keyword rankings, and overall SEO performance. You can also use it to conduct keyword research for Google, Amazon, and YouTube.
Getting Started with Ecommerce SEO
Rankings are never static, so ecommerce SEO is an ongoing process. However, the six steps outlined in this article will help you build a solid SEO foundation for your online store.
Keep your content original and in-depth, regularly check your site for technical issues, explore backlink opportunities, and always remember to find new keywords that fit your brand and products.
Ecommerce SEO FAQs
What is eCommerce SEO?
Ecommerce SEO is the process of making changes to your website to help your online store's web pages and product listings gain higher visibility on search engine results pages (aka SERPs).
How do I get ecommerce SEO results?
- Optimize your product titles and descriptions with relevant keywords.
- Write useful blog posts about your product, industry, or niche.
- To build the authority of your website, request backlinks from relevant websites.
- We regularly add new content to show that the website is active.
- We update our content regularly to keep it fresh and accurate.
Is SEO good for ecommerce?
SEO is a very powerful tool for ecommerce businesses. It helps increase organic traffic to your site, which can lead to greater visibility, more potential customers, and ultimately, more sales. SEO is also a cost-effective marketing strategy because it targets users who are already searching for your products online.
What is the difference between SEO and eCommerce SEO?
The basic principles of SEO and ecommerce SEO are the same. However, ecommerce SEO strategies are tailored to online stores. The main goal of ecommerce SEO is to increase visibility of products in search engine results to drive sales, while traditional SEO is to improve the visibility of website content to attract readers and interest. Tasks specific to ecommerce SEO include optimizing product pages and listings, and managing customer reviews.
How much does it cost to do SEO?
SEO costs vary depending on the size of your website and the scope of your SEO goals. However, many SEO tasks can be done for free. Keyword research, page optimization, content writing, and other tasks are essentially free and cost nothing other than the time you invest.
If you hire an SEO expert or agency, the cost will vary depending on their expertise, the size of your website, and the scope of services you need. Most businesses budget $1,500-$5,000 per month for external SEO projects.
Does Shopify do SEO automatically?
Shopify stores include SEO features to help you optimize your content. For example, you can create optimized product titles, descriptions, ALT text, and URLs. You can also leverage Shopify’s AI assistant to generate optimized content for your products. Other SEO features include submitting a sitemap to Google Search Console and creating a blog for your online store.
Adding a blog to your Shopify store can help you rank for relevant keywords that don’t compete with your product pages. For example, a Shopify store that sells birthday party supplies might rank for product-focused keywords like “balloons,” “streamers,” and “gifts.” Adding a few useful blog posts to your website can help you show up for other queries like “how to plan a birthday party.”
Is SEO worth considering on Shopify?
It’s important to consider SEO for your Shopify store. This will help you increase your visibility on search engine results pages (SERPs). Optimizing your Shopify store for users (creating pages that solve queries and gaining backlinks from relevant websites) will help you rank higher in results. This will help you rank more pages, attract customers by getting website traffic from organic search results, and reduce the cost of paid marketing.
